Head and Neck Cancer Surgeon In South Delhi
Head and neck cancers encompass a diverse group of uncommon tumors that frequently are aggressive in their biologic behavior. Moreover, patients with a history of head and neck cancer have the potential to develop a second primary tumor, generally due to the habitual use of tobacco.
Head and neck cancer refers to cancers that develop in the head and neck area,
including the mouth, throat, nose, sinuses, larynx, and salivary glands. It is often linked to lifestyle factors such as tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and
human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, particularly for cancers of the throat and
mouth. Symptoms can vary depending on the location of the cancer but
commonly include persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, unexplained
weight loss, hoarseness, or a lump in the neck.
Our Videos
Early detection is crucial, as head and neck cancers can often be treated successfully in the early stages. Diagnostic tests, such as physical exams, biopsies, and imaging scans, help determine the extent of the cancer. Treatment options typically include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, often in combination, depending on the cancer's stage and location. For cancers linked to HPV, immunotherapy may also be considered. While survival rates for head and neck cancer are improving, outcomes are better when the cancer is caught early and treated promptly. Regular screenings and reducing risk factors, like quitting smoking and limiting alcohol, can significantly lower the likelihood of developing head and neck cancers.
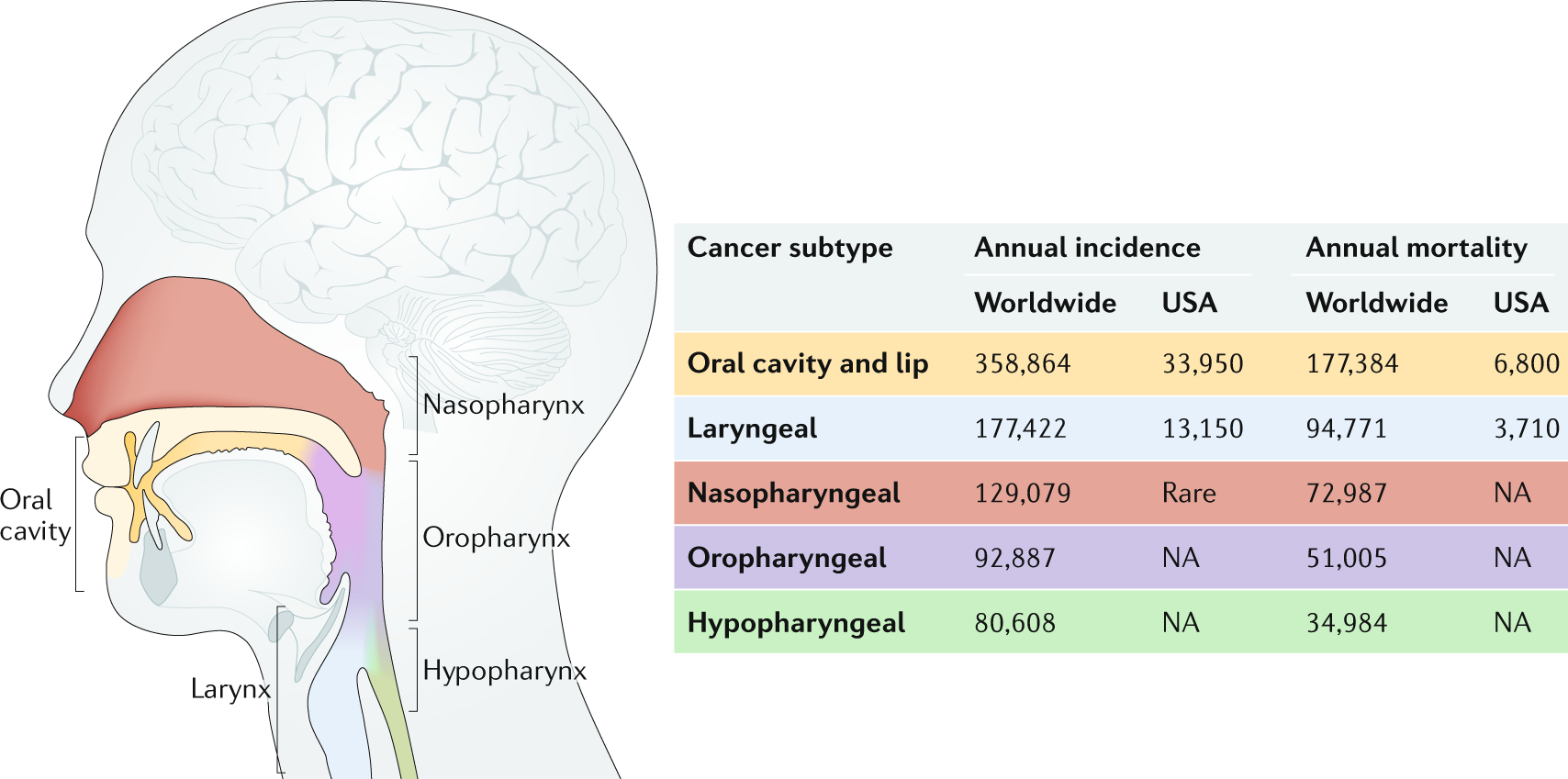
Types of Head and Neck Cancer
1. Oral Cancer2. Throat (Pharyngeal) Cancer
3. Laryngeal Cancer
4. Nasal and Paranasal Sinus Cancer
5. Salivary Gland Cancer
Causes and Risk Factors
- Tobacco and Alcohol Use: Major risk factors for most head and neck cancers.
- Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Linked to oropharyngeal cancers.
- Prolonged Sun Exposure: Increases the risk of lip and skin cancers.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: May contribute to the development of oral cancers.
- Exposure to Certain Chemicals: Such as asbestos and wood dust.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history can increase susceptibility.